What is Astigmatism?
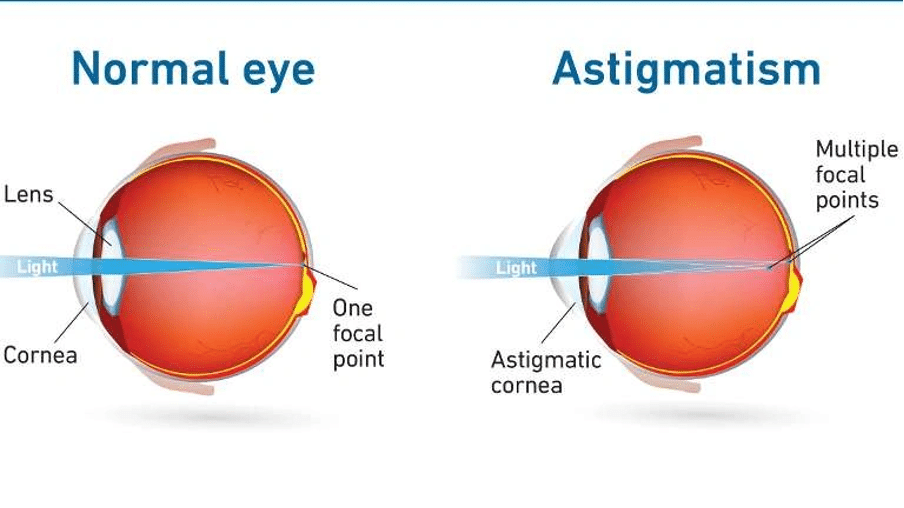
Astigmatism is a common vision condition caused by an irregular shape of the cornea or lens. Instead of having a perfectly round curvature, the eye is shaped more like a football, causing light to focus unevenly on the retina. This results in blurred or distorted vision at all distances.
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea or lens has an uneven curve. Because of this irregular shape, light entering the eye does not focus evenly on a single point on the retina, leading to blurry or distorted vision both near and far.

Astigmatism Causes and Risk Factors
Astigmatism is often present at birth and may be inherited. It can also develop after an eye injury, surgery, or due to certain eye conditions.
Common causes and risk factors include:
- Certain eye diseases
- Genetic factors
- Irregular corneal shape
- Eye trauma or surgery
Astigmatism Symptoms
Symptoms of astigmatism may vary depending on severity but commonly include blurred or distorted vision, eye strain, headaches, difficulty seeing at night, and frequent squinting to improve focus.

Childhood Astigmatism
Astigmatism can occur in children and may affect visual development if left uncorrected. Children with astigmatism may have trouble reading, focusing in school, or recognizing distant objects. Early detection through regular eye exams is essential to support healthy vision development.

Astigmatism Treatment
Astigmatism can usually be corrected with prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses designed to compensate for the irregular curvature of the eye. In some cases, refractive surgery such as LASIK may be an option for adults, depending on eye health and prescription stability.
An eye care professional can recommend the most appropriate treatment based on individual needs.
Sources:

