What is Farsightedness?
Farsightedness, also known as hyperopia, is a vision condition where distant objects may be seen clearly, but nearby objects appear blurry. This condition can affect people of all ages and may become more noticeable as the eyes age or are placed under visual strain.
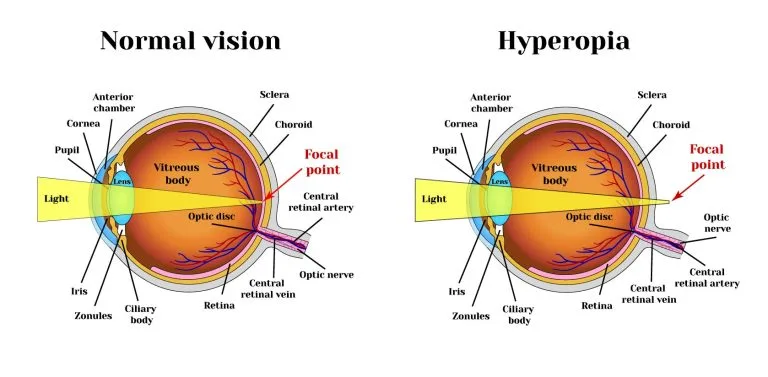
Farsightedness occurs when the eyeball is too short or the cornea has too little curvature. As a result, light entering the eye focuses behind the retina instead of directly on it, making close-up objects appear blurry while distant objects may remain clear.

Causes and Risk Factors of Farsightedness
Hyperopia is often caused by genetic factors, meaning it can run in families. Other contributing factors include abnormal eye shape, aging-related changes, and certain medical conditions affecting the eye’s structure.
Risk factors include:
- Eye development issues during childhood
- Family history of farsightedness
- Aging
Difference Between Farsightedness and Presbyopia
Although farsightedness and presbyopia both affect near vision, they are not the same condition. Farsightedness is related to the shape of the eye and can occur at any age. Presbyopia, on the other hand, is an age-related condition caused by the natural loss of lens flexibility, typically starting after age 40.
Farsightedness Symptoms
Common symptoms of farsightedness include difficulty focusing on nearby objects, eye strain, headaches, and fatigue after prolonged reading or screen use. Some people may also experience discomfort or burning sensations in the eyes.

Childhood Farsightedness
Mild farsightedness is common in young children and often improves as the eyes grow. However, significant hyperopia can interfere with learning and visual development if left untreated. Regular eye exams are essential to detect and manage farsightedness early.

Farsightedness Treatment
Treatment for farsightedness depends on the severity and the patient’s age. Common options include prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses to help focus light correctly onto the retina. In some cases, refractive surgery may be considered for adults.
An eye care professional can determine the most appropriate treatment based on individual vision needs.
Sources:
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/farsightedness/symptoms-causes/syc-20372495
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/hyperopia-farsightedness
- https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/farsightedness
- https://www.nei.nih.gov/eye-health-information/eye-conditions-and-diseases/farsightedness-hyperopia

